SurfaceNet+: An End-to-end 3D Neural Network for Very Sparse Multi-View Stereopsis
Mengqi Ji, Jinzhi Zhang, Qionghai Dai, Lu Fang.
IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence. 2020 May 25.
Introduction
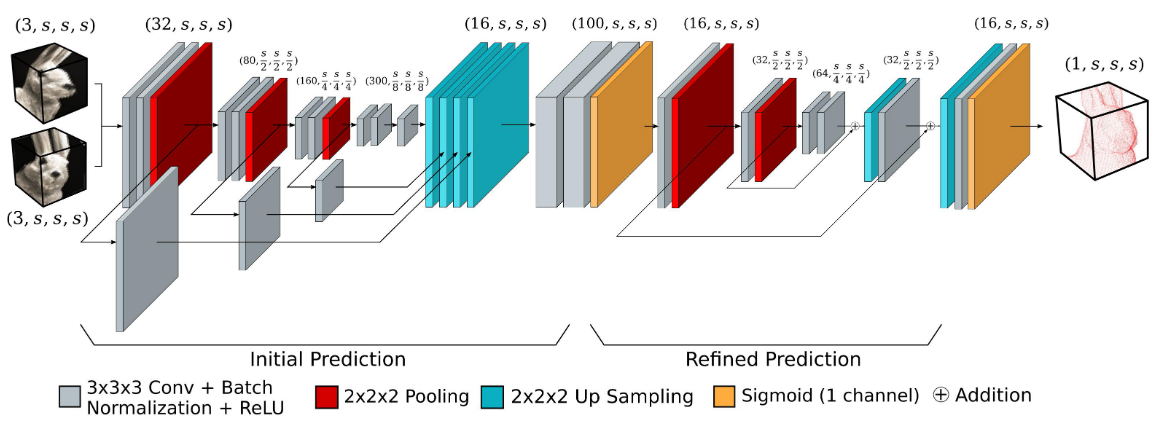
Multi-view stereopsis (MVS) tries to recover the 3D model from 2D mages. As the observations become sparser, the significant 3D information loss makes the MVS problem more challenging. Instead of only focusing on densely sampled conditions, we investigate sparse-MVS with large baseline angles since the sparser sensation is more practical and more cost-efficient. By investigating various observation sparsities, we show that the classical depth-fusion pipeline becomes powerless for the case with a larger baseline angle that worsens the photo-consistency check. As another line of the solution, we present SurfaceNet+, a volumetric method to handle the ‘incompleteness' and the ‘inaccuracy' problems induced by a very sparse MVS setup. Specifically, the former problem is handled by a novel volume-wise view selection approach. It owns superiority in selecting valid views while discarding invalid occluded views by considering the geometric prior. Furthermore, the latter problem is handled via a multi-scale strategy that consequently refines the recovered geometry around the region with the repeating pattern.
Citing
If you find our code useful, please kindly cite our paper:
@ARTICLE {9099504,
author = {M. Ji and J. Zhang and Q. Dai and L. Fang},
journal = {IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence},
title = {SurfaceNet+: An End-to-end 3D Neural Network for Very Sparse Multi-View Stereopsis},
year = {2021},
volume = {43},
number = {11},
issn = {1939-3539},
pages = {4078-4093},
keywords = {three-dimensional displays;cameras;surface reconstruction;two dimensional displays;solid modeling;geometry;image reconstruction},
doi = {10.1109/TPAMI.2020.2996798},
publisher = {IEEE Computer Society},
address = {Los Alamitos, CA, USA},
month = {nov}
}

